Interoperability
Interoperability (pronounced IHN-tuhr-AHP-uhr-uh-BIHL-ih-tee) is the ability of a system or a product to work with other systems or products without special effort on the part of the customer. Interoperability becomes a quality of increasing importance for information technology products as the concept that "The network is the computer" becomes a reality. For this reason, the term is widely used in product marketing descriptions.
Products achieve interoperability with other products using either or both of two approaches:
- By adhering to published interface standards
- By making use of a "broker" of services that can convert one product's interface into another product's interface "on the fly"
Compatibility is a related term. A product is compatible with a standard but interoperable with other products that meet the same standard (or achieve interoperability through a broker).
COMPONENTS
à DRDA
- Distributed Relational Database Architecture (DRDA) is a
database interoperability standard from The Open Group.
- DRDA describes the architecture for distributed relational
databases. It defines the rules for accessing the distributed data, but it does
not provide the actual application programming interfaces (APIs) to perform the
access. It was first used in DB2 2.3.
- DRDA was designed by a work group within IBM in the period
1988 to 1994. The messages, protocols, and structural components of DRDA are
defined by the IBM Distributed Data Management Architecture.
à RDA
- Remote database access (RDA) is a protocol standard for
database access.
- RDA describes the connection of a database client to a
database server. It includes features for
communicating database operations and parameters from the
client to the server,
in return, transporting result data from the server to the
client,
database transaction management.
exchange of information.
- RDA is an application-level protocol, inasmuch that it
builds on an existing network connection between client and server. In the case
of TCP/IP connections, RFC 1066 is used for implementing RDA.
à SOAP
- SOAP, originally an acronym for Simple Object Access
protocol, is a protocol specification for exchanging structured information in
the implementation of web services in computer networks. It uses XML
Information Set for its message format, and relies on other application layer
protocols, most notably Hypertext Transfer Protocol (H)
Database Interface
Working Principle of a Database Interface
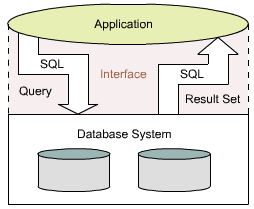 Working Principle of a Database Interface
Working Principle of a Database Interface
The
application poses with the help of SQL, a query language, a query to
the database system. There, the corresponding answer
(result set) is prepared and also with the help of
SQL given back to the application. This communication can take place
interactively
or be embedded into another language.
Type and Use of the Database Interface
Following, two important uses of a database interface like SQL are
listed:
| Interactive | SQL can be used interactively from a terminal. |
| Embedded | SQL can be embedded into another language (host language) which
might be used to create a database application |
User Interfaces
A user interface is
the view of a database interface that is seen by the user. User
interfaces are often graphical or at least
partly graphical (GUI - graphical user interface)
constructed and offer tools which make the interaction with the database
easier.
| Form-based Interfaces | This interface consist
of forms which are adapted to the user. He/She can fill in all of the
fields and make new entries to
the database or only some of the fields to
query the other ones. But some operations might be restricted by the
application.
Form-based user interfaces are wide spread and are a very important means of interacting with a DBMS. They are easy to use and have the advantage that the user does not need special knowledge about database languages like SQL. |
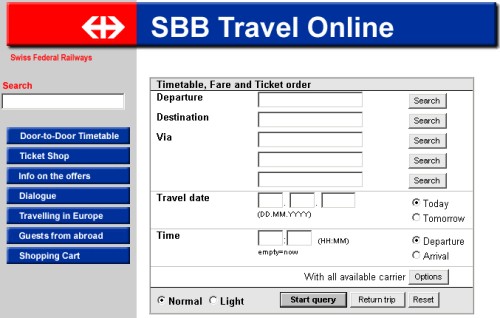 Example of a Form-based User Interface
Example of a Form-based User Interface| Text-based Interfaces | To be able to administrate the database or for other professional users there are possibilities to communicate with the DBMS
directly in the query language (in code form) via a input/output window.
We will see this possibility later in the lesson Structured Query Language SQL. Text-based interfaces are very powerful tools and allow a comprehensive interaction with a DBMS. However, the use of these is based on active knowledge of the respective database language. |
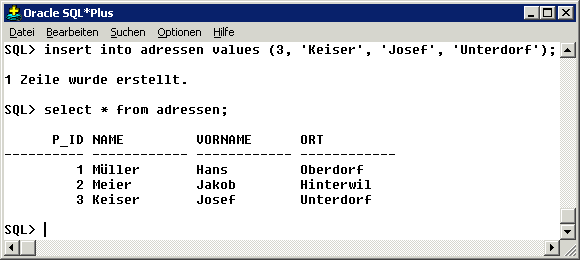 Example of a Text-base User Interface
Example of a Text-base User Interface| GIS Interface | A GIS user interface
often integrates features of a database interface. The database
interaction takes place through the combination
of different interfaces:
|
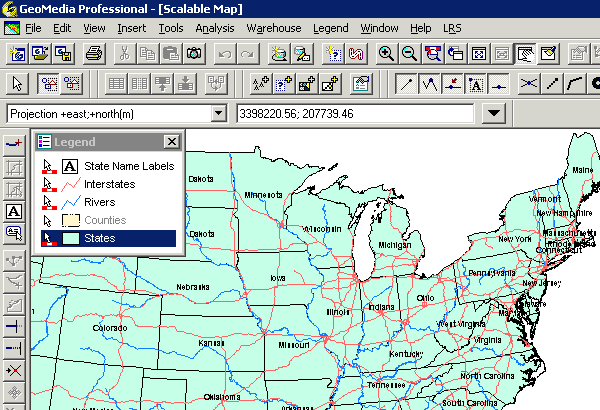 Example of a GIS Interface (GeoMedia, Intergraph)
Example of a GIS Interface (GeoMedia, Intergraph)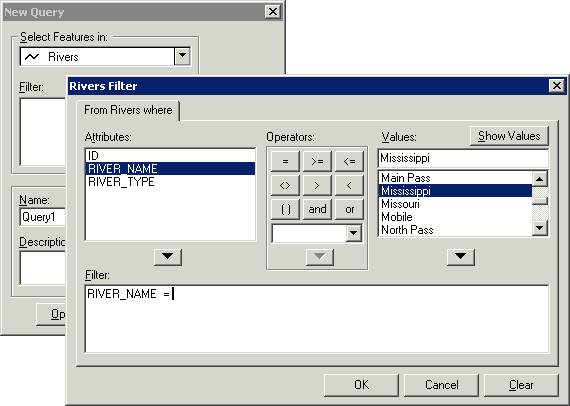
Example of a Query-Wizard within a GIS
INTERFACE
DEFINITION
- Capalibilities that provide systems capacity to support
the variousapplication environment being develop upon the database.
COMPONENTS
Extensible Markup Language (XML)
- is a markup language that defines a set of rules for
encoding documents in a format which is bothhuman-readable and
machine-readable. It is defined by the W3C's XML 1.0 Specification and by
several other related specifications, all of which are free open standards.
Universal Description, Discovery and Integration UDDI
- is a
platform-independent, Extensible Markup Language (XML)-based registry by which
businesses worldwide can list themselves on the Internet, and a mechanism to
register and locate web service applications. UDDI is an open industry
initiative, sponsored by the Organization for the Advancement of Structured
Information Standards (OASIS), for enabling businesses to publish service
listings and discover each other, and to define how the services or software applications
interact over the Internet.
WSDL
- WSDL is an XML format for describing network services as a
set of endpoints operating on messages containing either document-oriented or
procedure-oriented information. The operations and messages are described
abstractly, and then bound to a concrete network protocol and message format to
define an endpoint.
J2EE
- Java Platform, Enterprise Edition or Java EE is Oracle's
enterprise Java computing platform. The platform provides an API and runtime
environment for developing and running enterprise software, including network
and web services, and other large-scale, multi-tiered, scalable, reliable, and
secure network applications. Java EE extends the Java Platform, Standard
Edition (Java SE), providing an API for object-relational mapping, distributed
and multi-tier architectures, and web services.
Posted by Afiq Hakimi at 21:17 No comments:
Email ThisBlogThis!Share to TwitterShare to FacebookShare to
Pinterest
CONNECTIVITY
DEFINITION
-The Requireds compenents that allow client connection into
a database
COMPONENTS
REMOVE DATA OBJECT (RDO)
- Open Database Connectivity (ODBC) provides a set of
application programming interface (API) functions which make it easier for a
developer to connect to a wide range of database formats. ODBC gives the
developer a method of designing programs that are not specific to database format
whether you are using Oracle, SQL Server, Access, or others. ODBC drivers are
DLLs that contain the functions that let you connect to various databases. Each
ODBC driver is separate for each database format. ODBC drivers take the code
from a program and convert the functions to the specific database format being
used. RDO (Remote Data Objects) is a thin layer of code that acts as an ODBC
"wrapper", enabling the developer to invoke ODBC functionality using
familiar object method and property syntax.à SQL CALLS LEVEL INTERFACE
(SQL/CLI)
- The Call Level Interface (CLI) is an API and software
standard that embeds SQL code in a host program as defined in ISO/IEC
9075-3:2003.The Call Level Interface defines how a program should send SQL
queries to the database management system (DBMS) and how the returned
recordsets should be handled by the application in a consistent way. Developed
in the early 1990s, the API was defined only for the C and COBOL programming
languages.
The most widespread use of the CLI standard is the basis of
the ODBC (Open Database Connectivity) specification, which is widely used to
allow applications to transparently access database systems from different
vendors. The current version of the API, ODBC 3.52, incorporates features from
both the ISO and X/Open standards. Examples of languages that support Call
Level Interface are ANSI C, C#, VB.NET, Java, Pascal, and Fortran.
ACTIVEX DATA OBJECT (ADO)- In computing, Microsoft's
ActiveX Data Objects (ADO) comprises a set of Component Object Model (COM)
objects for accessing data sources. A part of MDAC (Microsoft Data Access
Components), it provides a middleware layer between programming languages and
OLE DB (a means of accessing data stores, whether databases or not, in a
uniform manner). ADO allows a developer to write programs that access data
without knowing how the database is implemented; developers must be aware of
the database for connection only. No knowledge of SQL is required to access a
database when using ADO, although one can use ADO to execute SQL commands
directly (with the disadvantage of introducing a dependency upon the type of
database used).
OBJECT LINK EMBEDDDING FOR DATABASE (OLE DB)- OLE DB an
API designed by Microsoft, allows accessing data from a variety of sources in a
uniform manner. The API provides a set of interfaces implemented using the
Component Object Model (COM); it is otherwise unrelated to OLE. Microsoft
originally intended OLE DB as a higher-level replacement for, and successor to,
ODBC, extending its feature set to support a wider variety of non-relational
databases, such as object databases and spreadsheets that do not necessarily
implement SQL.
à APPLICATION PROGRAMMING INTERFACE (API)- In computer
programming, an application programming interface (API) is a set of routines,
protocols, and tools for building software applications. An API expresses a
software component in terms of its operations, inputs, outputs, and underlying
types. An API defines functionalities that are independent of their respective
implementations, which allows definitions and implementations to vary without
compromising each other.
In addition to accessing databases or computer hardware,
such as hard disk drives or video cards, an API can ease the work of
programming GUI components. For example, an API can facilitate integration of
new features into existing applications (a so-called "plug-in API").
An API can also assist otherwise distinct applications with sharing data, which
can help to integrate and enhance the functionalities of the applications.
OPEN DATABASE CONNECTIVITY (ODBC)- A standard database
access method developed by the SQL Access group in 1992. The goal of ODBC is to
make it possible to access any data from any application, regardless of which
database management system (DBMS) is handling the data. ODBC manages this by
inserting a middle layer, called a database driver , between an application and
the DBMS. The purpose of this layer is to translate the application's data
queries into commands that the DBMS understands. For this to work, both the
application and the DBMS must be ODBC-compliant -- that is, the application
must be capable of issuing ODBC commands and the DBMS must be capable of
responding to them. Since version 2.0, the standard supports SAG SQL.
JAVA DATABASE CONNECTIVITY (JDBC)
- JDBC is a Java database connectivity technology (Java
Standard Edition platform) from Oracle Corporation. This technology is an API
for the Java programming language that defines how a client may access a
database. It provides methods for querying and updating data in a database.
JDBC is oriented towards relational databases. A JDBC-to-ODBC bridge enables
connections to any ODBC-accessible data source in the JVM host environment.
EMBEDED SQL FOR JAVA- SQLJ consists of a set of
programming extensions that define interaction between SQL and Java. It
comprises a set of clauses that extend Java programs to include static SQL
constructs. An SQLJ translator is a utility that transforms those SQLJ clauses
into standard Java code that accesses the database through a call interface.
The output of an SQLJ translator is a generated Java source program that can
then be compiled by any Java compiler. Java programs containing embedded SQL
can be subjected to static analysis of SQL statments for the purposes of syntax
checking, type checking and schema validation.
ACTIVEX DATA OBJECT (ADO)- In computing, Microsoft's
ActiveX Data Objects (ADO) comprises a set of Component Object Model (COM)
objects for accessing data sources. A part of MDAC (Microsoft Data Access Components),
it provides a middleware layer between programming languages and OLE DB (a
means of accessing data stores, whether databases or not, in a uniform manner).
ADO allows a developer to write programs that access data without knowing how
the database is implemented; developers must be aware of the database for
connection only. No knowledge of SQL is required to access a database when
using ADO, although one can use ADO to execute SQL commands directly (with the
disadvantage of introducing a dependency upon the type of database used).
No comments :
Post a Comment